PQSecure-HW™
High-Assurance, Side-Channel-Protected Cryptographic Hardware IP
PQSecure-HW™ delivers silicon-ready cryptographic IP cores for FPGA, ASIC, and SoC integration. Our portfolio spans Post-Quantum, Classical, Symmetric, and Lightweight primitives, engineered with integrated side-channel countermeasures and rigorous verification.
Complete Cryptographic Hardware Suite
Post-Quantum (NIST Standards)
ML-KEM (FIPS 203)
ML-DSA (FIPS 204)
SLH-DSA (FIPS 205)
FN-DSA / Falcon (FIPS 206 – coming soon)
* Supports NIST security levels 1, 3, and 5.
Stateful Hash-Based Signatures
XMSS (RFC 8391)
LMS / HSS (RFC 8554)
NIST SP 800-208
* Optimized for secure boot and firmware authentication.
Classical Public-Key
ECC: ECDSA, ECDH, Curve25519, Curve448, Ed25519, Ed448
RSA: 2048 / 3072 / 4096 (CRT Acceleration)
* Optional side-channel protection available.
Symmetric, Lightweight & Entropy
Symmetric: AES (GCM/CTR/CBC), SHA-2, SHA-3, HMAC
Lightweight: ASCON (AEAD/Hash/XOF), Trivium
Entropy: TRNG (SP 800-90B/C), DRBG
Deployment Targets
FPGA-Optimized IP
AMD / Xilinx (Artix, Kintex, UltraScale+, Versal) | Intel / Altera | Microchip | Menta-eFPGA | Analog Devices /Flex-Logix eFPGA
FPGA-proven and side-channel evaluated.
ASIC-Ready RTL
- Synthesizable Verilog / SystemVerilog
- Area, timing, and power optimized
- Technology-node portable
- EDA-flow compatible
SoC / Secure Enclave
- AXI / APB / TileLink interfaces
- RISC-V co-design ready
- Secure Boot integration
- Key provisioning interfaces
Built-In Side-Channel Protections
Security is embedded into the microarchitecture — not added afterward.
- Differential Power Analysis (DPA) resistance
- Correlation Power Analysis (CPA) mitigation
- First-order masking & shuffling techniques
- Constant-time hardware datapaths
- Fault injection countermeasures
- Glitch & EM-aware design
- FIPS-140-3 Ready: “non-invasive attacks” level 3+
Verification & Validation
- UVM-based verification environments
- RTL regression & constrained testing
- FPGA validation platforms
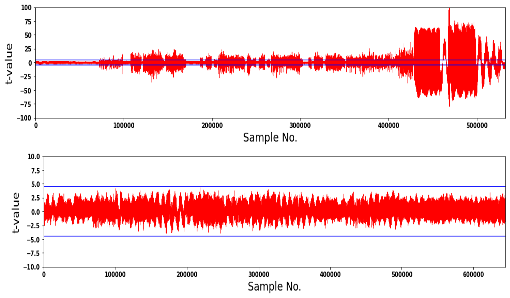
- TVLA-oriented leakage evaluation
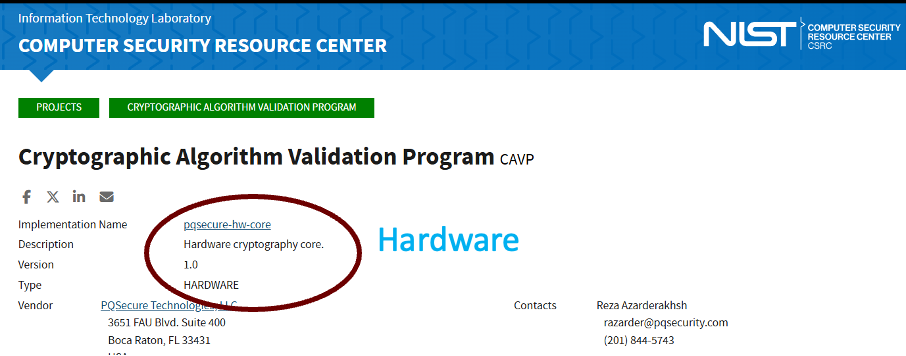
- ACVP / CAVP algorithm compliance
- NIST-KAT Test Vectors Benchmark
Hardware / Software Co-Design
Seamless integration with libpqsecure-C and libpqsecure-rs enabling:
- Hardware acceleration with secure software fallback
- Unified Root-of-Trust architectures
- Hybrid Classical + PQC deployments
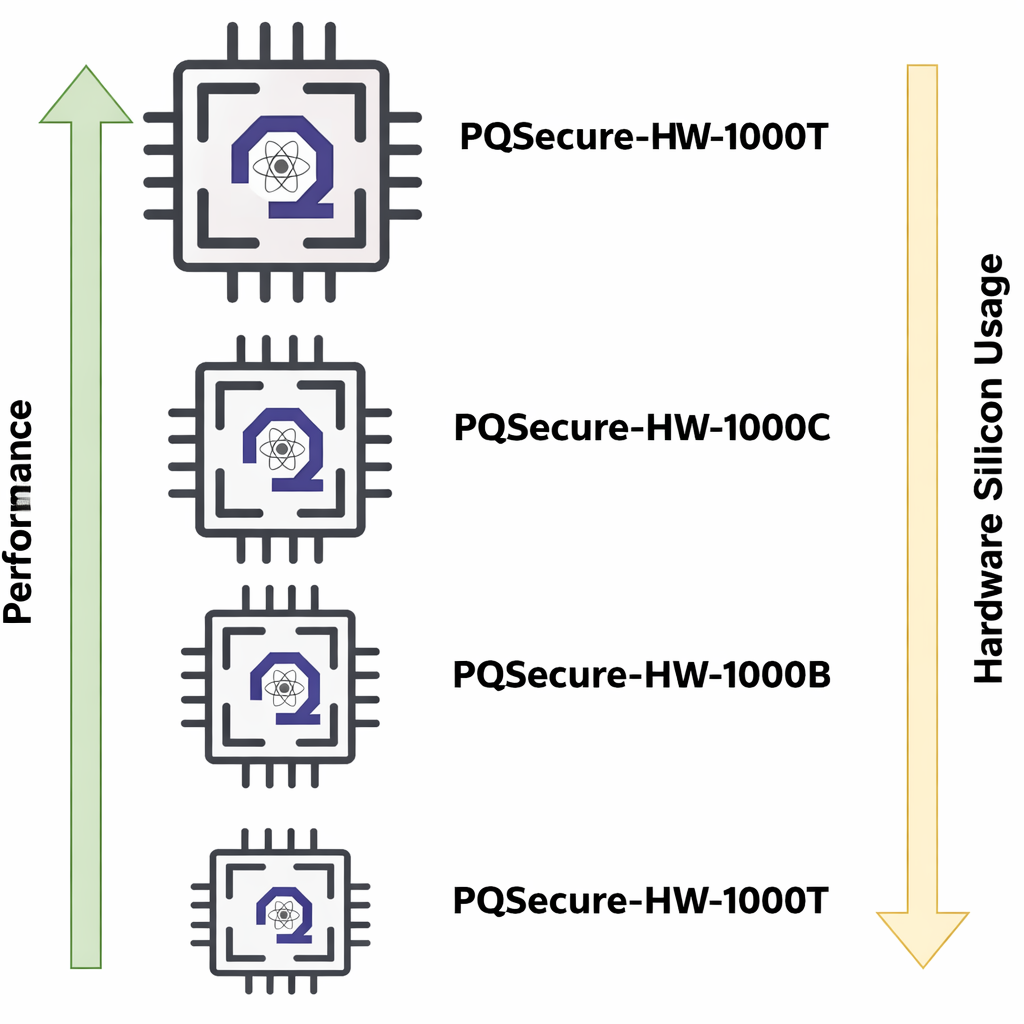
Configurable Architecture Profiles
Select the optimal balance of area, power, performance, and security.
- Smallest silicon area
- Reduced memory usage
- IoT endpoints
- Area-optimized
- Moderate throughput
- Power-sensitive
- Optimized tradeoff
- Secure gateways
- Defense platforms
- Parallel engines
- Deep pipelining
- Data center/cloud systems
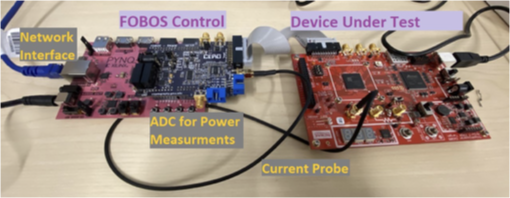
Independent Third-Party Evaluation
PQSecure-HW™ IP cores undergo independent evaluation through Keysight Device Vulnerability Analysis Services, a globally recognized provider of security validation and side-channel assessment.
Through third-party testing, PQSecure™ hardware implementations are evaluated for:
- Functional correctness validation
- Differential Power Analysis (DPA) assessment
- Correlation Power Analysis (CPA) leakage testing
- Electromagnetic (EM) side-channel analysis
- Fault injection susceptibility testing
- Implementation robustness under adversarial conditions
These independent evaluations complement our internal UVM verification, FPGA validation, and TVLA methodologies — providing additional assurance for defense, aerospace, and high-security deployments.